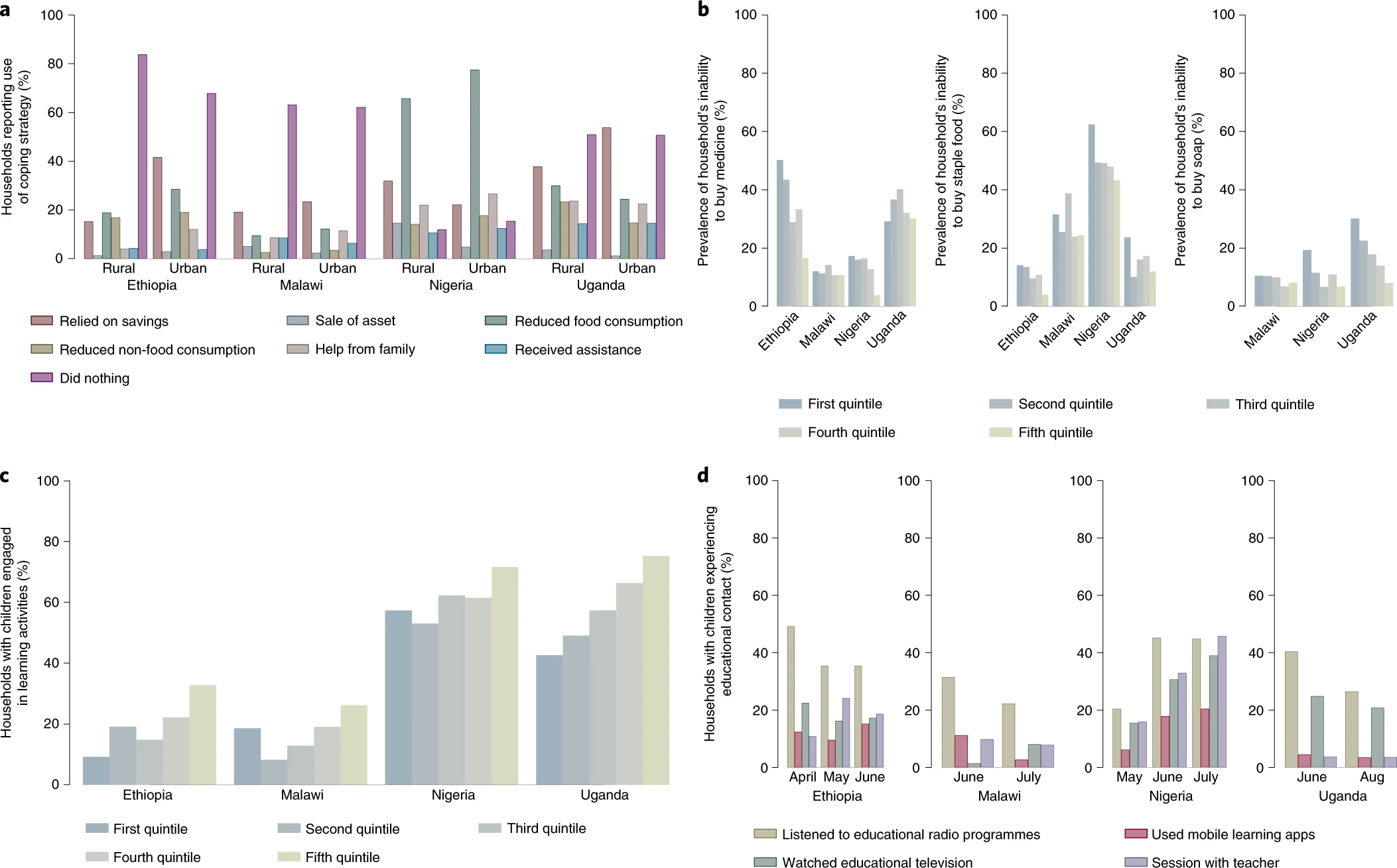
The emergence of SARS-CoV-2 and attempts to limit its spread have resulted in a contraction of the global economy. Here we document the socioeconomic impacts of the pandemic among households, adults and children in low-income countries. To do so, we rely on longitudinal household survey data from Ethiopia, Malawi, Nigeria and Uganda, originating from pre-COVID-19 face-to-face household surveys plus phone surveys [насколько пострадала репрезентативность?] implemented during the pandemic. We estimate that 256 million individuals—77% of the population—live in households that have lost income during the pandemic. Attempts to cope with this loss are exacerbated by food insecurity and an inability to access medicine and staple foods. Finally, we find that student–teacher contact has dropped from a pre-COVID-19 rate of 96% to just 17% among households with school-aged children. These findings can inform decisions by governments and international organizations on measures to mitigate the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic.
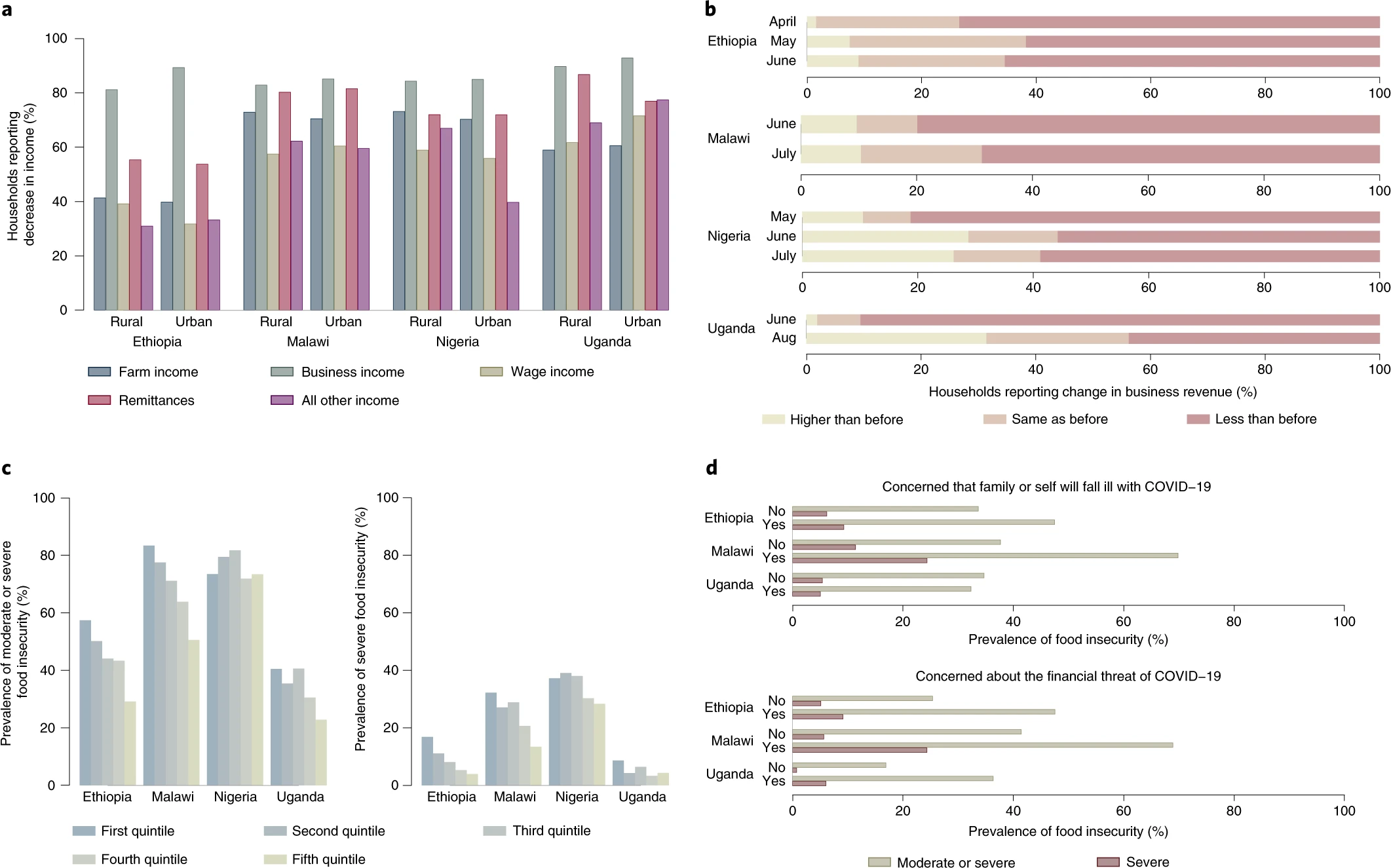 a, Percentage of households reporting loss of income sources, by country and rural or urban residence (n = 8,832). b, Percentage of households reporting change in business revenue, by country and round of survey (n = 4,357). c, Prevalence of moderate and/or severe food insecurity among adult individuals, by country and pre-COVID-19 household annual per capita consumption quintile (n = 8,711). d, Prevalence of food insecurity among adult individuals, by country and COVID-19-related concerns linked to health and finance (n = 8,816).
a, Percentage of households reporting loss of income sources, by country and rural or urban residence (n = 8,832). b, Percentage of households reporting change in business revenue, by country and round of survey (n = 4,357). c, Prevalence of moderate and/or severe food insecurity among adult individuals, by country and pre-COVID-19 household annual per capita consumption quintile (n = 8,711). d, Prevalence of food insecurity among adult individuals, by country and COVID-19-related concerns linked to health and finance (n = 8,816).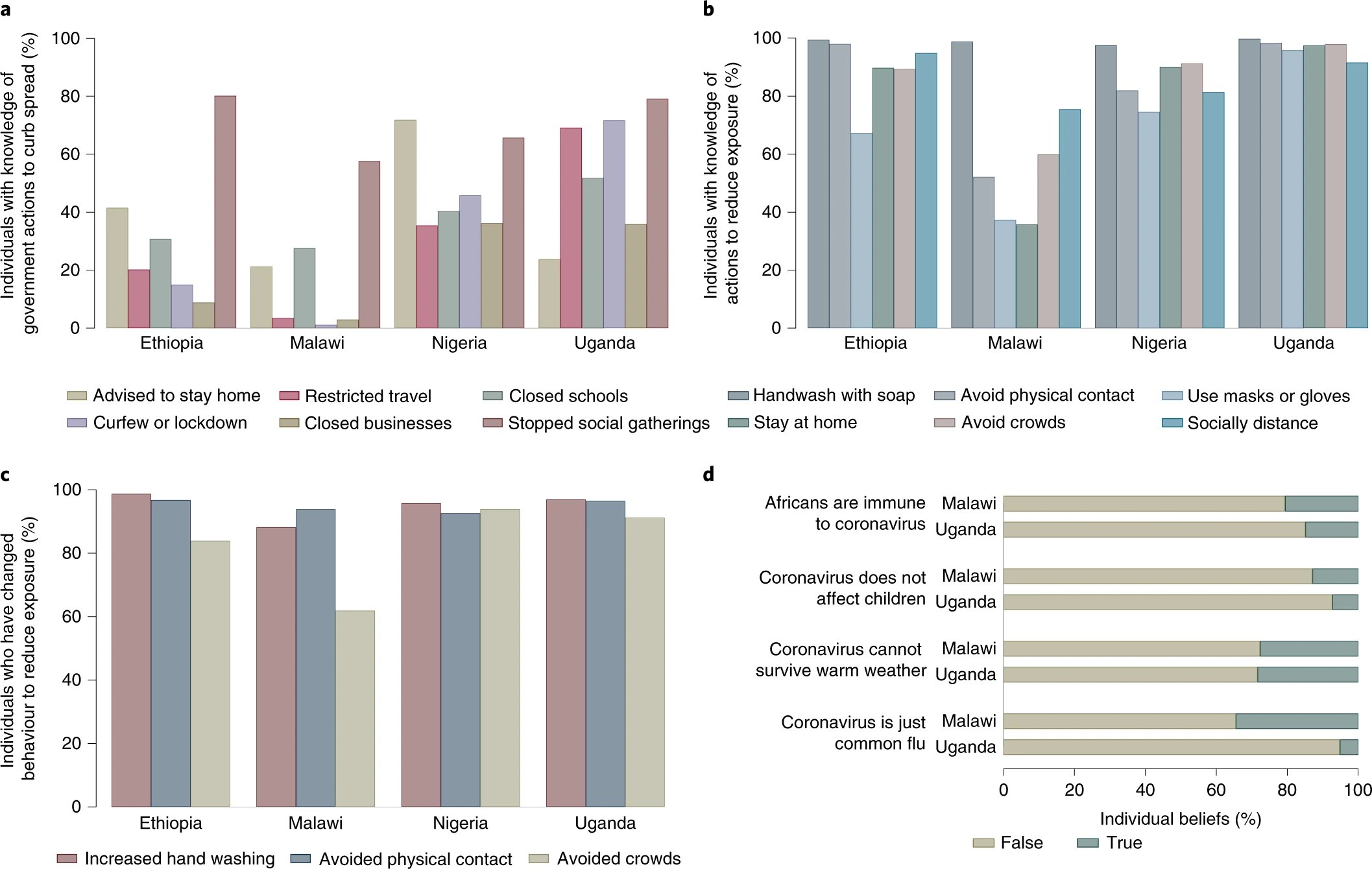
No comments:
Post a Comment