QuickStats: Percentage* of Adults† Aged ≥65 Years Meeting 2008 Federal Guidelines for Leisure-Time Aerobic§ and Muscle-Strengthening¶ Activities, by Age and Type of Activity — United States, 2000–2002 and 2013–2015
Weekly / September 23, 2016 / 65(37);1019
* With 95% confidence intervals indicated with error bars.
† Estimates are based on household interviews of a sample of the noninstitutionalized U.S. civilian population and are derived from the National Health Interview Survey sample adult component.
§ Performing at least 150 minutes (2 hours and 30 minutes) per week of moderate-intensity, or 75 minutes (1 hour and 15 minutes) per week of vigorous-intensity aerobic physical activity, or an equivalent combination of moderate/vigorous-intensity aerobic activity.
¶ Performing moderate/high intensity muscle-strengthening activities that involve all major muscle groups on ≥2 days per week.
From 2000–2002 to 2013–2015, the percentage of older adults who met the 2008 federal guidelines for aerobic activity increased from 35.7% to 42.5% among persons aged 65–74 years, from 24.5% to 30.9% among persons aged 75–84 years, and from 11.9% to 19.4% among persons aged ≥85 years. The percentage who met the guidelines for muscle strengthening activities increased from 11.7% to 19.3% among those aged 65–74 years, from 9.6% to 14.6% among those aged 75–84 years, and from 6.5% to 10.4% among those aged ≥85 years. In both periods, within each age group participation declined with age and was lower for muscle strengthening activities compared with aerobic activities.
Source: National Health Interview Survey; http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhis.htm.
Reported by: Yelena Gorina, MPH, MS, ygorina@cdc.gov, 301-458-4241.
* With 95% confidence intervals indicated with error bars.
† Estimates are based on household interviews of a sample of the noninstitutionalized U.S. civilian population and are derived from the National Health Interview Survey sample adult component.
§ Performing at least 150 minutes (2 hours and 30 minutes) per week of moderate-intensity, or 75 minutes (1 hour and 15 minutes) per week of vigorous-intensity aerobic physical activity, or an equivalent combination of moderate/vigorous-intensity aerobic activity.
¶ Performing moderate/high intensity muscle-strengthening activities that involve all major muscle groups on ≥2 days per week.
From 2000–2002 to 2013–2015, the percentage of older adults who met the 2008 federal guidelines for aerobic activity increased from 35.7% to 42.5% among persons aged 65–74 years, from 24.5% to 30.9% among persons aged 75–84 years, and from 11.9% to 19.4% among persons aged ≥85 years. The percentage who met the guidelines for muscle strengthening activities increased from 11.7% to 19.3% among those aged 65–74 years, from 9.6% to 14.6% among those aged 75–84 years, and from 6.5% to 10.4% among those aged ≥85 years. In both periods, within each age group participation declined with age and was lower for muscle strengthening activities compared with aerobic activities.
Source: National Health Interview Survey; http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhis.htm.
Reported by: Yelena Gorina, MPH, MS, ygorina@cdc.gov, 301-458-4241.
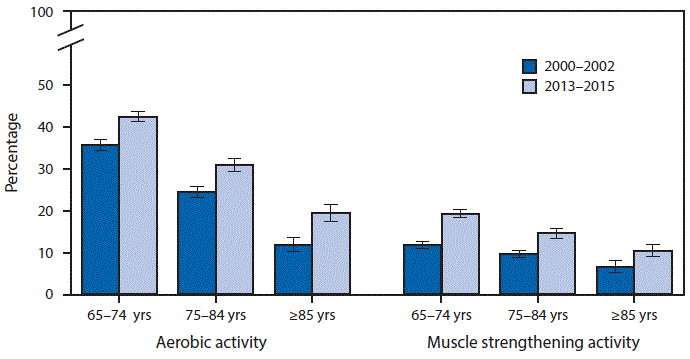
No comments:
Post a Comment